This picture shows the anatomical position.
The first directional term I am going to discuss is Superior and Inferior. Superior is up toward the head or the upper part of the body. For example the chest is superior to the knees.
Inferior in the opposite of superior so it is away from the head and towards the bottom part of the body. For example the toes are inferior to the belly button. Anterior is toward the front of the body or in front. An example would be the belly button is anterior of the spine. The opposite of Anterior would be Posterior. Posterior is towards the back of the body or in the behind. The heart is posterior to the breast bone would be an example of this. Medial is going towards the middle of the body so the heart would be medial to the shoulder.
Lateral is away from the medial or middle of the body so it would be going out towards the arms or shoulders. The fingers would be lateral to the heart is an example. Proximal is closer to the origin of a body part or an limb. Like the shoulder is proximal to the elbow. Distal is going farther away from the the origin like for example, the shin is distal to the knee. Superficial is toward the the body surface. An example is the skin is superficial to the skeleton. Deep is away form the body surface and is more toward the inner organs of the body. The Kidneys are deep to the skin would be a prime example of this.
The axial view of the body is the head neck and trunk area. This is the top of the body as seen in the picture above.
There are also Appendicular appendages or limb. One of these limbs would include the Brachial which is the arm.
The next classification of the body would be the body planes or the ways the body can be split. The first one would be sagittal which divides the body into left and right parts. If you were to cut a person in half using this plane you would have the left ear, eye,leg , and arm on one side and the right side of everything on the other side.
Frontal or Coronal Plan divides the body into anterior and posterior parts. This would be dividing the body from front to back. This will be shown wonderfully from the picture seen below.

Transverse or horizontal plane divides the body into superior or inferior parts. Simply put it is dividing the body from top and bottom. The last plane is the Oblique section and this is simply cuts that are made diagonally.
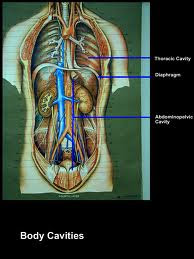
The next part of the body is the body cavities. The Dorsal cavity protects the sensitive nervous system and is divided into more subdivisions. The first division is the cranial cavity that is inside the skull and is what holds the brain. The other subdivision is the vertbral cavity and that is what holds the spinal cord.
This photo shows both of the Dorsal cavity subdivisions, the cranial and vertebral. As you can see the cranial cavity is on the head and is where the brain is held. the vertebral is on the back and is what holds the spine.
The ventral cavity holds the internal organs and just like the Dorsal cavity, has two subdivisions the thoracic and abdominopelvic.
From this picture you can infer that the ventral does indeed hold the internal organs and you can also see the two subdivisions.